Linear Momentum









Linear Momentum
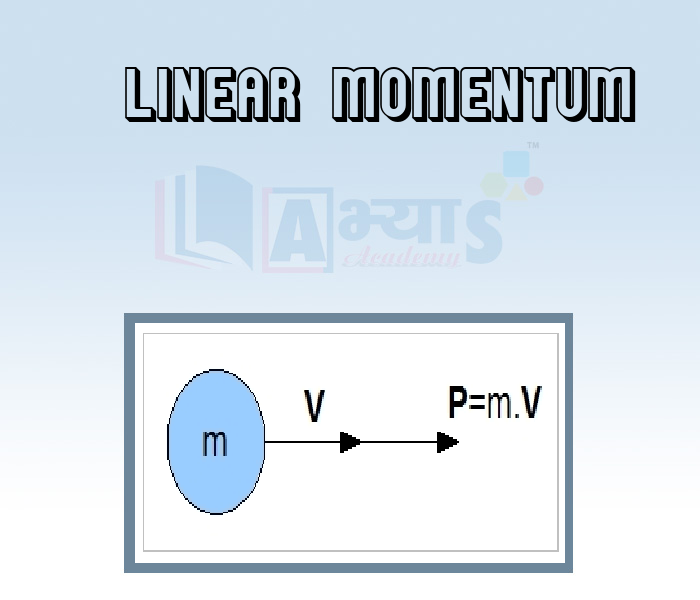
Momentum measures the quantity of motion possessed by a body. It is defined as the product of the mass of a body and its velocity. For a linear motion it is called the linear momentum of the body. It is the vector quantity which means that the body's momentum is always in the same direction as its velocity vector. It is a conserved quantity which means that the total momentum of the system is constant. If “m” is the mass and “v” be the velocity of a body at some instant, the linear momentum is given by the expression -
Here, p = momentum, v = velocity and m = mass
As momentum and velocity are the vector quantities therefore, they are denoted as and
respectively.
The SI unit of momentum is kg m/s
Examples:
1. A bullet fired at a wooden board can destroy it. But a small stone of the same mass as the bullet when thrown at the board will hardly cause any damage.Although their masses are the same, the high velocity of the bullet gives it a larger momentum, which causes the damage.
2.Consider, a truck and a rickshaw moving with the same velocities, heading towards each other and eventually ending up in a head on collision. The rickshaw could might get deformed to such an extend that it would be difficult for us to make it, while truck might get some minor damages.This is because of the larger momentum of the truck.
Illustration: A ball with a 500g mass is thrown with a velocity of 72 km/h. What is the initial momentum?
Solution: Given
mass of the ball = 500g = 0.5 Kg and
velocity of the ball = 72 km/h = 20 m/s
Momentum of the ball
Illustration: The linear momentum of a body is 40 kg m/s and the mass of the object is 5 kg. Determine the velocity of the object.
Solution: Given parameters are,
m = 5 kg and
p = 40 kg m/s
Linear momentum formula is given by
The momentum of a body of given mass is proportional to its | |||
| Right Option : C | |||
| View Explanation | |||
A body of mass 100 g is moving with a velocity of 15 m/s. The momentum associated with the ball will be | |||
| Right Option : B | |||
| View Explanation |
A Body of mass 25Kg collides against a wall with velocity 12 m/s and rebounds with the same speed. the change in momentum is | |||
| Right Option : D | |||
| View Explanation | |||
Students / Parents Reviews [10]
A marvelous experience with Abhyas. I am glad to share that my ward has achieved more than enough at the Ambala ABHYAS centre. Years have passed on and more and more he has gained. May the centre flourish and develop day by day by the grace of God.

Archit Segal
7thMy experience with Abhyas academy is very good. I did not think that my every subject coming here will be so strong. The main thing is that the online tests had made me learn here more things.

Hiya Gupta
8thBeing a parent, I saw my daughter improvement in her studies by seeing a good result in all day to day compititive exam TMO, NSO, IEO etc and as well as studies. I have got a fruitful result from my daughter.

Prisha Gupta
8thAbhyas Methodology is very good. It is based on according to student and each child manages accordingly to its properly. Methodology has improved the abilities of students to shine them in future.

Manish Kumar
10thMy experience with Abhyas is very good. I have learnt many things here like vedic maths and reasoning also. Teachers here first take our doubts and then there are assignments to verify our weak points.

Shivam Rana
7thIt has a great methodology. Students here can get analysis to their test quickly.We can learn easily through PPTs and the testing methods are good. We know that where we have to practice

Barkha Arora
10thMy experience was very good with Abhyas academy. I am studying here from 6th class and I am satisfied by its results in my life. I improved a lot here ahead of school syllabus.

Ayan Ghosh
8thI have spent a wonderful time in Abhyas academy. It has made my reasoning more apt, English more stronger and Maths an interesting subject for me. It has given me a habbit of self studying

Yatharthi Sharma
10thOne of the best institutes to develope a child interest in studies.Provides SST and English knowledge also unlike other institutes. Teachers are co operative and friendly online tests andPPT develope practical knowledge also.

Aman Kumar Shrivastava
10thIt was good as the experience because as we had come here we had been improved in a such envirnment created here.Extra is taught which is beneficial for future.
